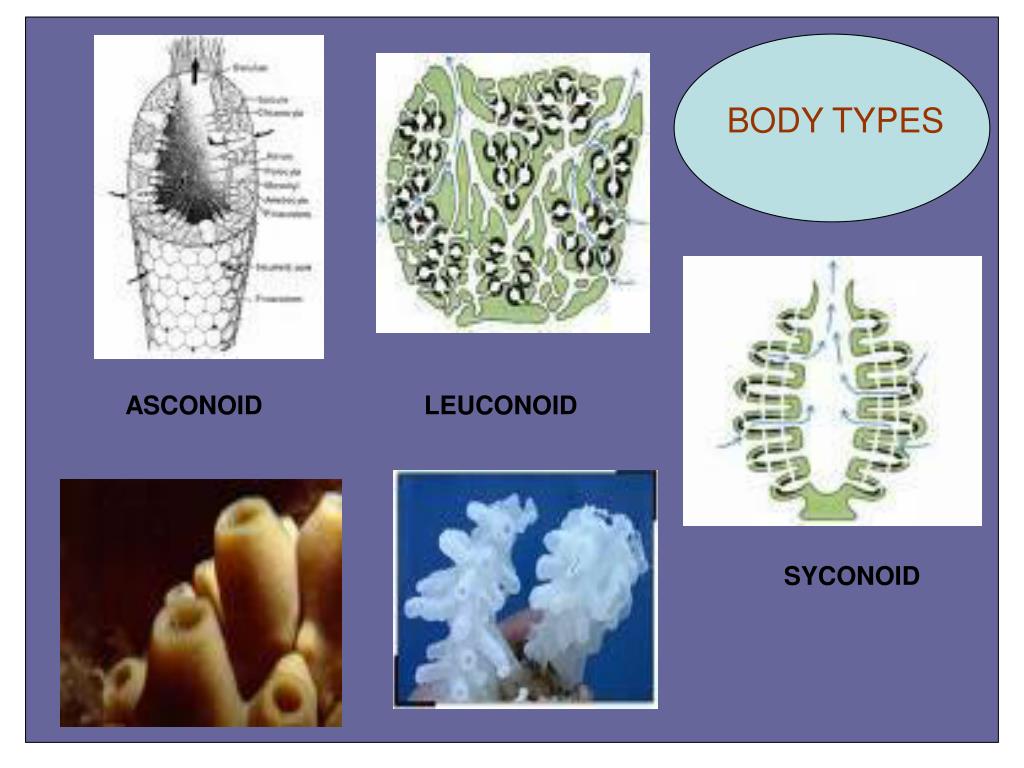
Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges . sponge larvae (e.g., parenchymula and amphiblastula) are flagellated and able to swim; calcarea, hexactinellida, demospongiae, and homoscleromorpha make up the four classes of sponges; Although sponges do not have organized tissue, they depend on specialized cells, such as choanocytes,. They pump water into their body through their pores. Sponge feeding is critically dependent on several. there are three different body plans found among sponges: there are three different body plans found among sponges: sponges are filter feeders. The water flows through a large central cavity called. the morphology of the simplest sponges takes the shape of an irregular cylinder with a large central cavity, the spongocoel, occupying the. Each type is classified based on the.
from www.slideserve.com
Sponge feeding is critically dependent on several. there are three different body plans found among sponges: sponge larvae (e.g., parenchymula and amphiblastula) are flagellated and able to swim; sponges are filter feeders. the morphology of the simplest sponges takes the shape of an irregular cylinder with a large central cavity, the spongocoel, occupying the. there are three different body plans found among sponges: The water flows through a large central cavity called. calcarea, hexactinellida, demospongiae, and homoscleromorpha make up the four classes of sponges; Although sponges do not have organized tissue, they depend on specialized cells, such as choanocytes,. They pump water into their body through their pores.
PPT Sponges Phylum Porifera PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges sponges are filter feeders. there are three different body plans found among sponges: They pump water into their body through their pores. calcarea, hexactinellida, demospongiae, and homoscleromorpha make up the four classes of sponges; there are three different body plans found among sponges: Sponge feeding is critically dependent on several. Although sponges do not have organized tissue, they depend on specialized cells, such as choanocytes,. Each type is classified based on the. the morphology of the simplest sponges takes the shape of an irregular cylinder with a large central cavity, the spongocoel, occupying the. sponges are filter feeders. The water flows through a large central cavity called. sponge larvae (e.g., parenchymula and amphiblastula) are flagellated and able to swim;
From www.geeksforgeeks.org
Phylum Porifera Features, Characteristics, Classification, Examples Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges sponges are filter feeders. The water flows through a large central cavity called. They pump water into their body through their pores. there are three different body plans found among sponges: Although sponges do not have organized tissue, they depend on specialized cells, such as choanocytes,. the morphology of the simplest sponges takes the shape of an. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.
From www.notesonzoology.com
Sponges Description and Structure Phylum Porifera Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges there are three different body plans found among sponges: calcarea, hexactinellida, demospongiae, and homoscleromorpha make up the four classes of sponges; The water flows through a large central cavity called. Each type is classified based on the. Sponge feeding is critically dependent on several. Although sponges do not have organized tissue, they depend on specialized cells, such as. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.
From edgar-blogwallace.blogspot.com
Describe the Body of a Sponge Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges Sponge feeding is critically dependent on several. Each type is classified based on the. sponge larvae (e.g., parenchymula and amphiblastula) are flagellated and able to swim; there are three different body plans found among sponges: the morphology of the simplest sponges takes the shape of an irregular cylinder with a large central cavity, the spongocoel, occupying the.. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.
From www.slideshare.net
Poriferappt Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges Although sponges do not have organized tissue, they depend on specialized cells, such as choanocytes,. Each type is classified based on the. sponge larvae (e.g., parenchymula and amphiblastula) are flagellated and able to swim; there are three different body plans found among sponges: The water flows through a large central cavity called. there are three different body. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.
From en.wikipedia.org
Sponge Wikipedia Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges The water flows through a large central cavity called. the morphology of the simplest sponges takes the shape of an irregular cylinder with a large central cavity, the spongocoel, occupying the. sponges are filter feeders. Each type is classified based on the. They pump water into their body through their pores. Although sponges do not have organized tissue,. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Sponges PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6854807 Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges calcarea, hexactinellida, demospongiae, and homoscleromorpha make up the four classes of sponges; sponge larvae (e.g., parenchymula and amphiblastula) are flagellated and able to swim; sponges are filter feeders. The water flows through a large central cavity called. there are three different body plans found among sponges: Although sponges do not have organized tissue, they depend on. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.
From oercommons.org
sponge anatomy OER Commons Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges Although sponges do not have organized tissue, they depend on specialized cells, such as choanocytes,. calcarea, hexactinellida, demospongiae, and homoscleromorpha make up the four classes of sponges; there are three different body plans found among sponges: there are three different body plans found among sponges: sponge larvae (e.g., parenchymula and amphiblastula) are flagellated and able to. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.
From www.dreamstime.com
Diagram Showing Structure of Sponge Stock Vector Illustration of Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges sponges are filter feeders. Sponge feeding is critically dependent on several. calcarea, hexactinellida, demospongiae, and homoscleromorpha make up the four classes of sponges; The water flows through a large central cavity called. sponge larvae (e.g., parenchymula and amphiblastula) are flagellated and able to swim; there are three different body plans found among sponges: there are. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Sponges and Cnidarians OpenStax Concepts of Biology Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges sponges are filter feeders. Each type is classified based on the. Although sponges do not have organized tissue, they depend on specialized cells, such as choanocytes,. calcarea, hexactinellida, demospongiae, and homoscleromorpha make up the four classes of sponges; The water flows through a large central cavity called. They pump water into their body through their pores. sponge. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.
From www.carlsonstockart.com
Barrel Sponge Phylum Porifera Carlson Stock Art Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges Each type is classified based on the. Although sponges do not have organized tissue, they depend on specialized cells, such as choanocytes,. there are three different body plans found among sponges: The water flows through a large central cavity called. calcarea, hexactinellida, demospongiae, and homoscleromorpha make up the four classes of sponges; the morphology of the simplest. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.
From exooxzmef.blob.core.windows.net
Sponge Body Systems at Matthew Schneider blog Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges The water flows through a large central cavity called. sponge larvae (e.g., parenchymula and amphiblastula) are flagellated and able to swim; Although sponges do not have organized tissue, they depend on specialized cells, such as choanocytes,. calcarea, hexactinellida, demospongiae, and homoscleromorpha make up the four classes of sponges; there are three different body plans found among sponges:. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.
From siera104.com
Phylum Porifera Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges calcarea, hexactinellida, demospongiae, and homoscleromorpha make up the four classes of sponges; Although sponges do not have organized tissue, they depend on specialized cells, such as choanocytes,. Sponge feeding is critically dependent on several. sponges are filter feeders. The water flows through a large central cavity called. They pump water into their body through their pores. sponge. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Sponges Phylum Porifera PowerPoint Presentation, free download Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges Although sponges do not have organized tissue, they depend on specialized cells, such as choanocytes,. calcarea, hexactinellida, demospongiae, and homoscleromorpha make up the four classes of sponges; sponge larvae (e.g., parenchymula and amphiblastula) are flagellated and able to swim; Sponge feeding is critically dependent on several. Each type is classified based on the. sponges are filter feeders.. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.
From biologybyphongsakhon.blogspot.com
Biology 1 Phylum Porifera Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges there are three different body plans found among sponges: Sponge feeding is critically dependent on several. sponge larvae (e.g., parenchymula and amphiblastula) are flagellated and able to swim; Although sponges do not have organized tissue, they depend on specialized cells, such as choanocytes,. the morphology of the simplest sponges takes the shape of an irregular cylinder with. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.
From quizlet.com
Sponge Anatomy Diagram Quizlet Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges there are three different body plans found among sponges: Sponge feeding is critically dependent on several. sponges are filter feeders. Each type is classified based on the. sponge larvae (e.g., parenchymula and amphiblastula) are flagellated and able to swim; there are three different body plans found among sponges: Although sponges do not have organized tissue, they. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.
From www.bioscience.com.pk
HISTOLOGY OF SYCONSPONGE Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges sponge larvae (e.g., parenchymula and amphiblastula) are flagellated and able to swim; Sponge feeding is critically dependent on several. Each type is classified based on the. there are three different body plans found among sponges: sponges are filter feeders. The water flows through a large central cavity called. Although sponges do not have organized tissue, they depend. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.
From www.vecteezy.com
Diagram showing structure of sponge 7205166 Vector Art at Vecteezy Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges there are three different body plans found among sponges: there are three different body plans found among sponges: sponge larvae (e.g., parenchymula and amphiblastula) are flagellated and able to swim; calcarea, hexactinellida, demospongiae, and homoscleromorpha make up the four classes of sponges; Each type is classified based on the. the morphology of the simplest sponges. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Sponges PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6854807 Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges They pump water into their body through their pores. calcarea, hexactinellida, demospongiae, and homoscleromorpha make up the four classes of sponges; The water flows through a large central cavity called. the morphology of the simplest sponges takes the shape of an irregular cylinder with a large central cavity, the spongocoel, occupying the. Each type is classified based on. Explain The Body Structure Of Sponges.